Oats are often hailed as a superfood—packed with fiber, vitamins, and heart-healthy benefits. But what happens when you eat them every single day? While oats are nutritious, overconsumption can lead to digestive issues, nutrient imbalances, and even weight gain in some cases.
In this article, we’ll explore the lesser-known disadvantages of daily oat consumption, backed by science and expert opinions. Whether you’re an oatmeal lover or just health-conscious, this guide will help you make informed dietary choices.
7 Disadvantages of Eating Oats Every Day
1. Digestive Issues (Bloating & Gas)
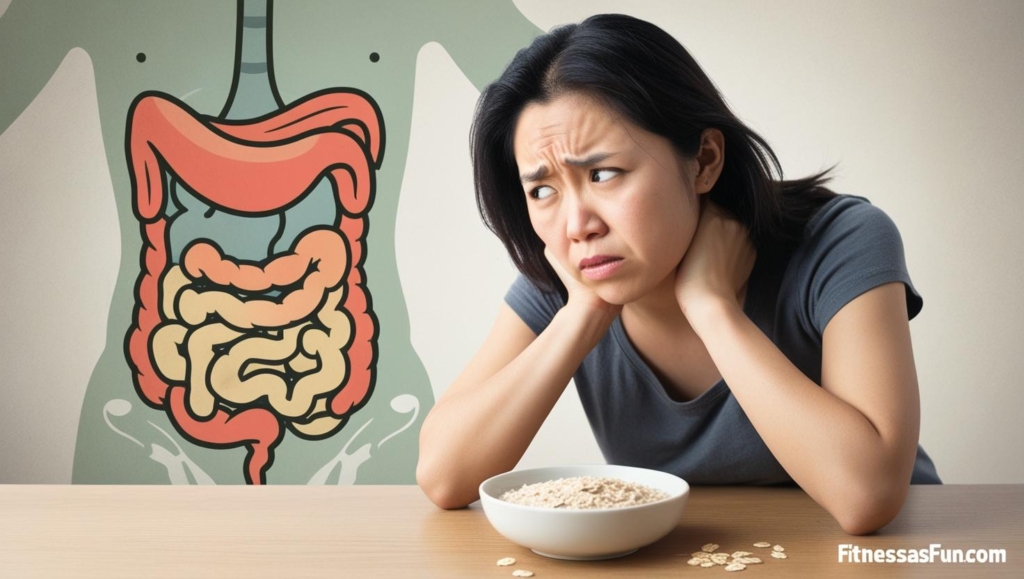

Oats are high in fiber (especially soluble fiber like beta-glucan), which can cause:
✔ Bloating
✔ Excessive gas
✔ Stomach cramps (in sensitive individuals)
A *2021 study in the Journal of Nutrition found that sudden increases in fiber intake can disrupt gut bacteria balance, leading to discomfort.
2. Blood Sugar Spikes (For Some People)
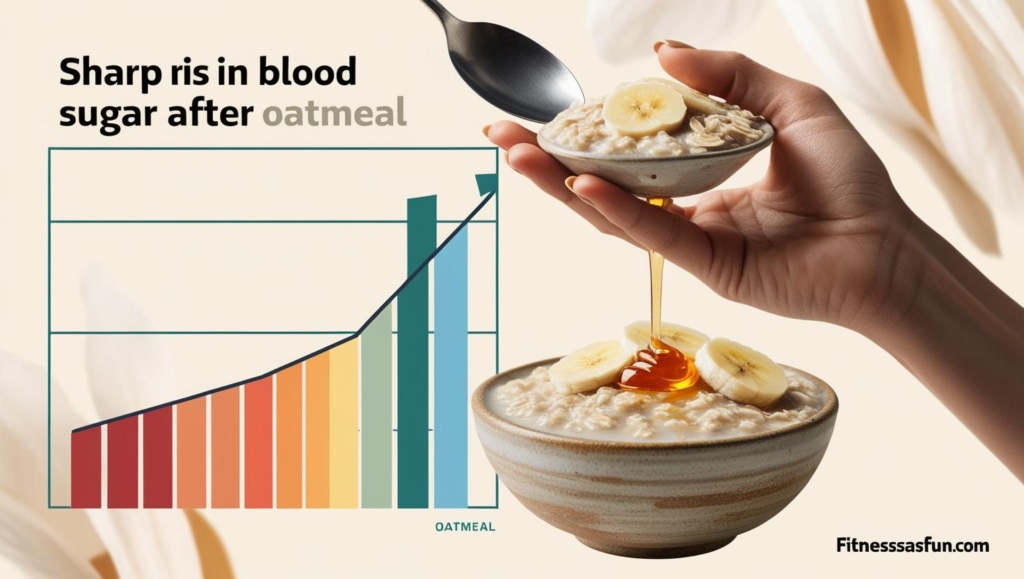
While oats are low-glycemic, processed varieties (instant oats, flavored packets) can spike blood sugar due to:
✔ Added sugars
✔ Lack of protein/fat to slow digestion
A Harvard Health report (2023) notes that instant oatmeal has a higher glycemic index (GI) than steel-cut oats.
3. Nutrient Deficiencies (If Over-Relied On)

Eating oats too frequently may lead to:
✔ Iron & zinc deficiencies (oats contain phytates, which block mineral absorption)
✔ Low protein intake (oats only provide ~5g per serving)
✔ Lack of dietary variety (missing other essential nutrients)
4. Weight Gain (When Portions Aren’t Controlled)

A bowl of oats is healthy—until you add:
✔ Excessive sweeteners (honey, syrup)
✔ High-calorie toppings (nuts, dried fruit, peanut butter)
✔ Oversized servings (some people eat 2-3 cups in one sitting)
5. Gluten Cross-Contamination (For Celiac Patients)

Even “gluten-free” oats can be contaminated during processing. A Celiac Disease Foundation (2022) report warns that 5-10% of celiac patients react to oats.
6. May Trigger IBS Symptoms
For those with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), oats (especially high-FODMAP varieties) can worsen:
✔ Diarrhea
✔ Abdominal pain
✔ Constipation (if fiber intake isn’t balanced with water)
7. Pesticide Residue Concerns
Conventional oats often contain glyphosate, a controversial herbicide. The EWG (2023) found alarming levels in popular oat brands.
How to Eat Oats Safely (Minimizing Risks)
✔ Choose organic oats (lower pesticide risk)
✔ Opt for steel-cut or rolled oats (lower GI than instant)
✔ Balance with protein/fat (add nuts, seeds, or Greek yogurt)
✔ Soak oats overnight (reduces phytates for better nutrient absorption)
✔ Rotate with other breakfasts (quinoa, eggs, chia pudding)
FAQ: Your Oatmeal Questions Answered
1. Can oats cause constipation?
Yes, if you don’t drink enough water. Fiber needs fluids to move smoothly.
2. Are oats bad for weight loss?
No, but portion control matters. Stick to ½ cup dry oats per serving.
3. Do oats cause inflammation?
Usually no—but flavored oats with sugar might. Plain oats are anti-inflammatory.
4. How much oatmeal is too much?
More than 1 cup dry oats daily may lead to bloating or nutrient issues.
5. Are overnight oats healthier?
Yes! Soaking reduces phytates and improves digestion.
Conclusion
Oats are nutritious, but daily consumption isn’t for everyone. Digestive sensitivity, blood sugar concerns, and nutrient-blocking compounds mean moderation is key.
Try alternating oats with other healthy breakfasts to keep your diet balanced.
Do you eat oats daily? Have you experienced any side effects? Share your thoughts below!
Sources
- Harvard Health (2023) – “Glycemic Index of Oats”
- Celiac Disease Foundation (2022) – “Oats and Gluten Sensitivity”
- EWG (2023) – “Glyphosate in Oat Products”
- Journal of Nutrition (2021) – “Fiber and Gut Health”