Most people blame a “slow metabolism” when fat loss stalls.
But here’s the truth: Your metabolism isn’t broken—it’s misunderstood.
Let’s cut through the noise and debunk the biggest metabolism myths so you can focus on what actually moves the needle.
First, What Is Metabolism?
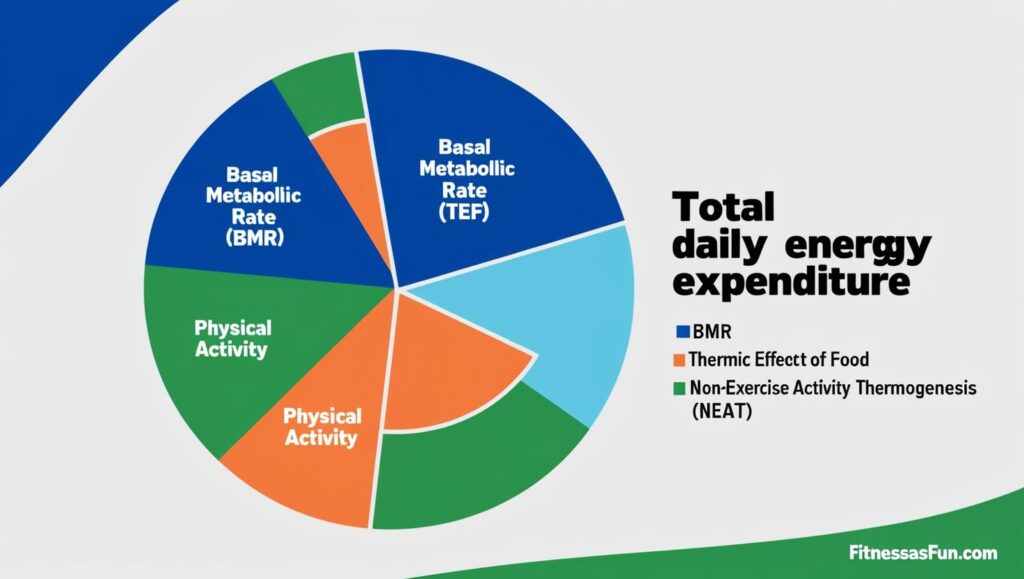
Metabolism is the sum of all the processes your body uses to convert food into energy.
It includes:
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): Energy needed just to survive (breathing, organ function)
- Thermic Effect of Food (TEF): Energy used to digest food
- Physical Activity: Exercise + daily movement
- Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT): Fidgeting, walking, chores
Your BMR is the biggest slice—up to 70% of your daily calorie burn.
Now let’s separate fact from fiction.
Myth #1: Thin People Have Faster Metabolisms

False.
In fact, larger individuals tend to have higher BMRs because they have more body mass to maintain.
✅ Muscle mass, not just body weight, is the real metabolism booster.
Myth #2: Your Metabolism Crashes After 30
Not entirely.
Metabolism slightly slows with age—but the real culprit is often muscle loss and less activity.
Here’s what helps:
- Strength training
- Adequate protein
- Staying active daily
✅ Age is a factor, but habits matter more.
Myth #3: Eating Small Meals Speeds Up Metabolism
Wrong again.
Meal frequency has zero effect on your metabolism.
What matters is your total calorie intake and nutrient quality.
✅ You can eat 2 or 6 meals a day—your body doesn’t care.
Myth #4: Starving Yourself Will “Shut Down” Metabolism
Partially true—but misleading.
Severe calorie restriction slows metabolism over time through adaptive thermogenesis.
But it doesn’t “shut down”—your body just becomes more efficient to conserve energy.
✅ Long-term extreme dieting is the real danger—not short-term deficits.
Myth #5: Cardio Is the Best Way to Boost Metabolism
Not entirely.
Cardio burns calories during the workout. But resistance training builds muscle, which increases your resting metabolic rate (RMR).
✅ Muscle = long-term metabolic investment.
Myth #6: Your Metabolism Is Genetic—Nothing You Can Do
Yes, genetics play a role.
But lifestyle controls far more than you think.
What you can control:
- Your muscle mass
- Activity levels
- Sleep quality
- Stress management
- Food choices
✅ Your daily actions override a sluggish gene card.
Personal Note: How I Reset My Own Metabolism

I used to think I had a slow metabolism. I’d eat 1,400 calories a day and still gain weight.
The turning point?
- I stopped the extreme dieting
- Focused on resistance training
- Added more protein
- Walked 10,000+ steps/day
- Slept 7-8 hours
After 3 months, not only did my body composition change, but I was eating 2,200+ calories and still leaning out.
✅ I didn’t speed up my metabolism—I just stopped slowing it down.
So, What Really Affects Metabolic Rate?

Here’s what matters most:
- Muscle mass (build more of it)
- Sleep (deep, uninterrupted sleep regulates metabolism hormones)
- Daily movement (NEAT matters more than your gym session)
- Protein intake (higher TEF)
- Stress (cortisol can mess with your hunger and fat storage)
- Consistency (your metabolism loves rhythm)
FAQs
Q: Can drinking cold water boost metabolism?
Barely. It burns a few extra calories, but the effect is negligible.
Q: What foods speed up metabolism?
No food “speeds up” metabolism dramatically. But high-protein foods and spicy meals slightly raise TEF.
Q: Do metabolism boosters work?
Most supplements are overhyped. Caffeine can help a bit, but lifestyle wins in the long run.
Q: Is a slow metabolism to blame for weight gain?
Usually not. Overeating and under-moving are more common causes.






